Which Are The Principal Causes Of Adult Aquired FlatFeet ?
Overview
Have you noticed the arch in your foot collapse over a fairly short period of time as an adult? Or Do you suffer from pain on the inside and sole of your arch? If it does, then you may be suffering from a condition known as adult acquired flat foot. As one of the main support structures of the foot?s arch, the tibilais posterior tendon, along with other muscles, tendons and ligaments, play a very important role in its mechanical function.
Causes
Flat feet causes greater pressure on the posterior tibial tendon than normal. As the person with flat feet ages, the muscles, tendons and ligaments weaken. Blood supplies diminish as arteries narrow. These conditions are magnified for obese patients because of their increased weight and atherosclerosis. Finally, the tendon gives out or tears. Most of the time, this is a slow process. Once the posterior tibial tendon and ligaments stretch, body weight causes the bones of the arch to move out of position. The foot rotates inward (pronation), the heel bone is tilted to the inside, and the arch appears collapsed. In some cases, the deformity progresses until the foot dislocates outward from the ankle joint.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling around the inside aspect of the ankle initially. Later, the arch of the foot may fall (foot becomes flat), this change leads to walking to become difficult and painful, as well as standing for long periods. As the flat foot becomes established, pain may progress to the outer part of the ankle. Eventually, arthritis may develop.
Diagnosis
In the early stages of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, most of the discomfort is located medially along the course of the tendon and the patient reports fatigue and aching on the plantar-medial aspect of the foot and ankle. Swelling is common if the dysfunction is associated with tenosynovitis. As dysfunction of the tendon progresses, maximum pain occurs laterally in the sinus tarsi because of impingement of the fibula against the calcaneus. With increasing deformity, patients report that the shape of the foot changes and that it becomes increasingly difficult to wear shoes. Many patients no longer report pain in the medial part of the foot and ankle after a complete rupture of the posterior tibial tendon has occurred; instead, the pain is located laterally. If a fixed deformity has not occurred, the patient may report that standing or walking with the hindfoot slightly inverted alleviates the lateral impingement and relieves the pain in the lateral part of the foot.
Non surgical Treatment
Although AAF is not reversible without surgery, appropriate treatment should address the patient?s current symptoms, attempt to reduce pain, and allow continued ambulation. In the early stages, orthotic and pedorthic solutions can address the loss of integrity of the foot?s support structures, potentially inhibiting further destruction.3-5 As a general principle, orthotic devices should only block or limit painful or destructive motion without reducing or restricting normal motion or muscle function. Consequently, the treatment must match the stage of the deformity.

Surgical Treatment
For more chronic flatfoot pain, surgical intervention may be the best option. Barring other serious medical ailments, surgery is a good alternative for patients with a serious problem. There are two surgical options depending on a person?s physical condition, age and lifestyle. The first type of surgery involves repair of the PTT by transferring of a nearby tendon to help re-establish an arch and straighten out the foot. After this surgery, patients wear a non-weight bearing support boot for four to six weeks. The other surgery involves fusing of two or three bones in the hind foot below the ankle. While providing significant pain relief, this option does take away some hind foot side-to-side motion. Following surgery, patients are in a cast for three months. Surgery is an effective treatment to address adult-acquired flatfoot, but it can sometimes be avoided if foot issues are resolved early. That is why it is so important to seek help right away if you are feeling ankle pain. But perhaps the best way to keep from becoming flatfooted is to avoid the risk factors altogether. This means keeping your blood pressure, weight and diabetes in check.
Have you noticed the arch in your foot collapse over a fairly short period of time as an adult? Or Do you suffer from pain on the inside and sole of your arch? If it does, then you may be suffering from a condition known as adult acquired flat foot. As one of the main support structures of the foot?s arch, the tibilais posterior tendon, along with other muscles, tendons and ligaments, play a very important role in its mechanical function.

Causes
Flat feet causes greater pressure on the posterior tibial tendon than normal. As the person with flat feet ages, the muscles, tendons and ligaments weaken. Blood supplies diminish as arteries narrow. These conditions are magnified for obese patients because of their increased weight and atherosclerosis. Finally, the tendon gives out or tears. Most of the time, this is a slow process. Once the posterior tibial tendon and ligaments stretch, body weight causes the bones of the arch to move out of position. The foot rotates inward (pronation), the heel bone is tilted to the inside, and the arch appears collapsed. In some cases, the deformity progresses until the foot dislocates outward from the ankle joint.
Symptoms
Pain and swelling around the inside aspect of the ankle initially. Later, the arch of the foot may fall (foot becomes flat), this change leads to walking to become difficult and painful, as well as standing for long periods. As the flat foot becomes established, pain may progress to the outer part of the ankle. Eventually, arthritis may develop.
Diagnosis
In the early stages of dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon, most of the discomfort is located medially along the course of the tendon and the patient reports fatigue and aching on the plantar-medial aspect of the foot and ankle. Swelling is common if the dysfunction is associated with tenosynovitis. As dysfunction of the tendon progresses, maximum pain occurs laterally in the sinus tarsi because of impingement of the fibula against the calcaneus. With increasing deformity, patients report that the shape of the foot changes and that it becomes increasingly difficult to wear shoes. Many patients no longer report pain in the medial part of the foot and ankle after a complete rupture of the posterior tibial tendon has occurred; instead, the pain is located laterally. If a fixed deformity has not occurred, the patient may report that standing or walking with the hindfoot slightly inverted alleviates the lateral impingement and relieves the pain in the lateral part of the foot.
Non surgical Treatment
Although AAF is not reversible without surgery, appropriate treatment should address the patient?s current symptoms, attempt to reduce pain, and allow continued ambulation. In the early stages, orthotic and pedorthic solutions can address the loss of integrity of the foot?s support structures, potentially inhibiting further destruction.3-5 As a general principle, orthotic devices should only block or limit painful or destructive motion without reducing or restricting normal motion or muscle function. Consequently, the treatment must match the stage of the deformity.

Surgical Treatment
For more chronic flatfoot pain, surgical intervention may be the best option. Barring other serious medical ailments, surgery is a good alternative for patients with a serious problem. There are two surgical options depending on a person?s physical condition, age and lifestyle. The first type of surgery involves repair of the PTT by transferring of a nearby tendon to help re-establish an arch and straighten out the foot. After this surgery, patients wear a non-weight bearing support boot for four to six weeks. The other surgery involves fusing of two or three bones in the hind foot below the ankle. While providing significant pain relief, this option does take away some hind foot side-to-side motion. Following surgery, patients are in a cast for three months. Surgery is an effective treatment to address adult-acquired flatfoot, but it can sometimes be avoided if foot issues are resolved early. That is why it is so important to seek help right away if you are feeling ankle pain. But perhaps the best way to keep from becoming flatfooted is to avoid the risk factors altogether. This means keeping your blood pressure, weight and diabetes in check.
What Exactly Will Cause Tendinitis Discomfort In The Achilles ?
Overview
 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
Causes
When you place a large amount of stress on your Achilles tendon too quickly, it can become inflamed from tiny tears that occur during the activity. Achilles tendonitis is often a result of overtraining, or doing too much too soon. Excessive hill running can contribute to it. Flattening of the arch of your foot can place you at increased risk of developing Achilles tendonitis because of the extra stress placed on your Achilles tendon when walking or running.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain in the heel and along the tendon when walking or running. The area may feel painful and stiff in the morning. The tendon may be painful to touch or move. The area may be swollen and warm. You may have trouble standing up on one toe.
Diagnosis
Examination of the achilles tendon is inspection for muscle atrophy, swelling, asymmetry, joint effusions and erythema. Atrophy is an important clue to the duration of the tendinopathy and it is often present with chronic conditions. Swelling, asymmetry and erythema in pathologic tendons are often observed in the examination. Joint effusions are uncommon with tendinopathy and suggest the possibility of intra-articular pathology. Range of motion testing, strength and flexibility are often limited on the side of the tendinopathy. Palpation tends to elicit well-localized tenderness that is similar in quality and location to the pain experienced during activity. Physical examinations of the Achilles tendon often reveals palpable nodules and thickening. Anatomic deformities, such as forefoot and heel varus and excessive pes planus or foot pronation, should receive special attention. These anatomic deformities are often associated with this problem. In case extra research is wanted, an echography is the first choice of examination when there is a suspicion of tendinosis. Imaging studies are not necessary to diagnose achilles tendonitis, but may be useful with differential diagnosis. Ultrasound is the imaging modality of first choice as it provides a clear indication of tendon width, changes of water content within the tendon and collagen integrity, as well as bursal swelling. MRI may be indicated if diagnosis is unclear or symptoms are atypical. MRI may show increased signal within the Achilles.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Achilles tendinitis can typically be treated at home by following the R.I.C.E. treatment method. Rest. Rest the tendon by avoiding activities that irritate the tendon or increase swelling. However, this does not mean you should be completely inactive for long periods of time, as this can cause stiffness in your joints. It?s still important to stretch in order to maintain strength and flexibility and partake in activities that don?t put direct pressure on the tendon, such as bicycling. Ice. Apply ice to the affected area for 20-minutes at a time, every couple hours, as needed, to reduce swelling and pain. Compression. Use compression bandages to help reduce swelling. Elevation. Elevate your ankle above the level of your heart to help reduce swelling. It is particularly important to do this at night while you sleep. Simply place a pillow or two under your ankle to keep it elevated. Once the tendon has healed, be sure to gradually return to more strenuous activities. If flattened arches contributed to the injury, wear shoes with appropriate support or inserts to prevent the condition from progressing or recurring. If these non-surgical treatments have not been able to provide relief of symptoms after several months, surgery may be performed to remove inflamed tissue. However, this is not usually recommended unless all other options have been exhausted. Consult your doctor for more information about surgical treatment options.

Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery you will have depends on the type of injury you are faced with. The longer you have waited to have surgery will also be a factor that determines what type of surgery is needed. With acute (recent) tearing the separation in your Achilles tendon is likely to be very minimal. If you have an acute tear you may qualify for less invasive surgery (such as a mini-open procedure). Surgeons will always choose a shorter, less invasive procedure if it is possible to do so. Most surgeons know that a less complicated procedure will have less trauma to the tendon and a much quicker rate of recovery after the surgery.
Prevention
To lower your risk of Achilles tendonitis, stretch your calf muscles. Stretching at the beginning of each day will improve your agility and make you less prone to injury. You should also try to stretch both before and after workouts. To stretch your Achilles, stand with a straight leg, and lean forward as you keep your heel on the ground. If this is painful, be sure to check with a doctor. It is always a good idea to talk to your doctor before starting a new exercise routine. Whenever you begin a new fitness regimen, it is a good idea to set incremental goals. Gradually intensifying your physical activity is less likely to cause injury. Limiting sudden movements that jolt the heels and calves also helps to reduce the risk of Achilles tendonitis. Try combining both high- and low-impact exercises in your workouts to reduce stress on the tendon. For example, playing basketball can be combined with swimming. It doesn?t matter if you?re walking, running, or just hanging out. To decrease pressure on your calves and Achilles tendon, it?s important to always wear the right shoes. That means choosing shoes with proper cushioning and arch support. If you?ve worn a pair of shoes for a long time, consider replacing them or using arch supports. Some women feel pain in the Achilles tendon when switching from high heels to flats. Daily wearing of high heels can both tighten and shorten the Achilles tendon. Wearing flats causes additional bending in the foot. This can be painful for the high-heel wearer who is not accustomed to the resulting flexion. One effective strategy is to reduce the heel size of shoes gradually. This allows the tendon to slowly stretch and increase its range of motion.
 The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
The Achilles tendon connects the calf muscle to the back of the heel. Injuries to the Achilles tendon are common, as it is in constant use during walking and running. These injuries, known as Achilles tendinitis, are usually the result of overuse damage and minor tears that have accumulated over years. Your risk of developing Achilles tendinitis increases with age and activity level. Many athletes develop Achilles tendinitis. The tendon may be injured several inches away from where it attaches to the foot or at the point of attachment. An injury at the point of attachment is called Achilles enthesopathy. We recommend a combination of treatments over a period of months that may include wearing supportive shoes or orthotic devices, performing stretching exercises, and icing the affected area. If these treatments are not effective, or if the tendon is completely torn, we may recommend surgery.
Causes
When you place a large amount of stress on your Achilles tendon too quickly, it can become inflamed from tiny tears that occur during the activity. Achilles tendonitis is often a result of overtraining, or doing too much too soon. Excessive hill running can contribute to it. Flattening of the arch of your foot can place you at increased risk of developing Achilles tendonitis because of the extra stress placed on your Achilles tendon when walking or running.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain in the heel and along the tendon when walking or running. The area may feel painful and stiff in the morning. The tendon may be painful to touch or move. The area may be swollen and warm. You may have trouble standing up on one toe.
Diagnosis
Examination of the achilles tendon is inspection for muscle atrophy, swelling, asymmetry, joint effusions and erythema. Atrophy is an important clue to the duration of the tendinopathy and it is often present with chronic conditions. Swelling, asymmetry and erythema in pathologic tendons are often observed in the examination. Joint effusions are uncommon with tendinopathy and suggest the possibility of intra-articular pathology. Range of motion testing, strength and flexibility are often limited on the side of the tendinopathy. Palpation tends to elicit well-localized tenderness that is similar in quality and location to the pain experienced during activity. Physical examinations of the Achilles tendon often reveals palpable nodules and thickening. Anatomic deformities, such as forefoot and heel varus and excessive pes planus or foot pronation, should receive special attention. These anatomic deformities are often associated with this problem. In case extra research is wanted, an echography is the first choice of examination when there is a suspicion of tendinosis. Imaging studies are not necessary to diagnose achilles tendonitis, but may be useful with differential diagnosis. Ultrasound is the imaging modality of first choice as it provides a clear indication of tendon width, changes of water content within the tendon and collagen integrity, as well as bursal swelling. MRI may be indicated if diagnosis is unclear or symptoms are atypical. MRI may show increased signal within the Achilles.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Achilles tendinitis can typically be treated at home by following the R.I.C.E. treatment method. Rest. Rest the tendon by avoiding activities that irritate the tendon or increase swelling. However, this does not mean you should be completely inactive for long periods of time, as this can cause stiffness in your joints. It?s still important to stretch in order to maintain strength and flexibility and partake in activities that don?t put direct pressure on the tendon, such as bicycling. Ice. Apply ice to the affected area for 20-minutes at a time, every couple hours, as needed, to reduce swelling and pain. Compression. Use compression bandages to help reduce swelling. Elevation. Elevate your ankle above the level of your heart to help reduce swelling. It is particularly important to do this at night while you sleep. Simply place a pillow or two under your ankle to keep it elevated. Once the tendon has healed, be sure to gradually return to more strenuous activities. If flattened arches contributed to the injury, wear shoes with appropriate support or inserts to prevent the condition from progressing or recurring. If these non-surgical treatments have not been able to provide relief of symptoms after several months, surgery may be performed to remove inflamed tissue. However, this is not usually recommended unless all other options have been exhausted. Consult your doctor for more information about surgical treatment options.

Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery you will have depends on the type of injury you are faced with. The longer you have waited to have surgery will also be a factor that determines what type of surgery is needed. With acute (recent) tearing the separation in your Achilles tendon is likely to be very minimal. If you have an acute tear you may qualify for less invasive surgery (such as a mini-open procedure). Surgeons will always choose a shorter, less invasive procedure if it is possible to do so. Most surgeons know that a less complicated procedure will have less trauma to the tendon and a much quicker rate of recovery after the surgery.
Prevention
To lower your risk of Achilles tendonitis, stretch your calf muscles. Stretching at the beginning of each day will improve your agility and make you less prone to injury. You should also try to stretch both before and after workouts. To stretch your Achilles, stand with a straight leg, and lean forward as you keep your heel on the ground. If this is painful, be sure to check with a doctor. It is always a good idea to talk to your doctor before starting a new exercise routine. Whenever you begin a new fitness regimen, it is a good idea to set incremental goals. Gradually intensifying your physical activity is less likely to cause injury. Limiting sudden movements that jolt the heels and calves also helps to reduce the risk of Achilles tendonitis. Try combining both high- and low-impact exercises in your workouts to reduce stress on the tendon. For example, playing basketball can be combined with swimming. It doesn?t matter if you?re walking, running, or just hanging out. To decrease pressure on your calves and Achilles tendon, it?s important to always wear the right shoes. That means choosing shoes with proper cushioning and arch support. If you?ve worn a pair of shoes for a long time, consider replacing them or using arch supports. Some women feel pain in the Achilles tendon when switching from high heels to flats. Daily wearing of high heels can both tighten and shorten the Achilles tendon. Wearing flats causes additional bending in the foot. This can be painful for the high-heel wearer who is not accustomed to the resulting flexion. One effective strategy is to reduce the heel size of shoes gradually. This allows the tendon to slowly stretch and increase its range of motion.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is sometimes mixed up with a heel spur although they are not the same. A heel spur is a calcium deposit that occurs where the plantar fascia is attached to the heel bone (calcaneus). In many cases a heel spur is found on a foot with no pain or other symptoms at all. And in many painful heels there is no sign for a heel spur. Heel spur and painful heal does not necessarily go together. For many years plantar fasciitis was believed to be an inflammatory condition. It is thought now to be inaccurate because there were many cases of the disorder with no inflammatory signs observed within the fascia. The heel pain cause is now believed to be damage to the collagen fibers of the fascia. This damage, caused by stress injury, sometimes may include inflammatory cells.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the thick band of tissue on the bottom of the foot is overstretched or overused. This can be painful and make walking more difficult. You are more likely to get plantar fasciitis if you Have foot arch problems (both flat feet and high arches), run long distances, downhill or on uneven surfaces, are obese or gain weight suddenly, have a tight Achilles tendon (the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel), wear shoes with poor arch support or soft soles. Plantar fasciitis is seen in both men and women. However, it most often affects active men ages 40 - 70. It is one of the most common orthopedic foot complaints. Plantar fasciitis was commonly thought to be caused by a heel spur. However, research has found that this is not the case. On x-ray, heel spurs are seen in people with and without plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is usually found in one foot. While bilateral plantar fasciitis is not unheard of, this condition is more the result of a systemic arthritic condition that is extremely rare in an athletic population. There is a greater incidence of plantar fasciitis in males than females (Ambrosius 1992). While no direct cause could be found it could be argued that males are generally heavier which, when combined with the greater speeds, increased ground contact forces, and less flexibility, may explain the greater injury predisposition. The most notable characteristic of plantar fasciitis is pain upon rising, particularly the first step out of bed. This morning pain can be located with pinpoint accuracy at the bony landmark on the anterior medial tubercle of the calcaneus. The pain may be severe enough to prevent the athlete from walking barefooted in a normal heel-toe gait. Other less common presentations include referred pain to the subtalar joint, the forefoot, the arch of the foot or the achilles tendon (Brantingham 1992). After several minutes of walking the pain usually subsides only to re turn with the vigorous activity of the day's training session. The problem should be obvious to the coach as the athlete will exhibit altered gait and/ or an abnormal stride pattern, and may complain of foot pain during running/jumping activities. Consistent with plantar fascia problems the athlete will have a shortened gastroc complex. This can be evidenced by poor dorsiflexion (lifting the forefoot off the ground) or inability to perform the "flying frog" position. In the flying frog the athlete goes into a full squat position and maintains balance and full ground contact with the sole of the foot. Elevation of the heel signifies a tight gastroc complex. This test can be done with the training shoes on.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check your feet and watch you stand and walk. He or she will also ask questions about your past health, including what illnesses or injuries you have had. Your symptoms, such as where the pain is and what time of day your foot hurts most. How active you are and what types of physical activity you do. Your doctor may take an X-ray of your foot if he or she suspects a problem with the bones of your foot, such as a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment initially involves offloading the plantar fascia by aoiding aggravating factors, such as running. Taping, this can work very well to alleviate pain, and can be almost immediate. It isn't a long-term solution, but can relieve symptoms in the beginning. Using a night splint to stretch the calf, so that less load is placed on the plantar fascia (if tightness in the calf is a factor). Using a gel heel cup, this can act to increase shock absorption, and by raising the heel there is also less stretch on the calf. So, temporarily, this may relieve pain in someone who has a tight calf. Massage, but this depends if the plantarfascia is actually tight or just painful. If it is tight, then massage can temporarily relieve the pain, but if it is irritated then taping and corrective footwear is preferable.
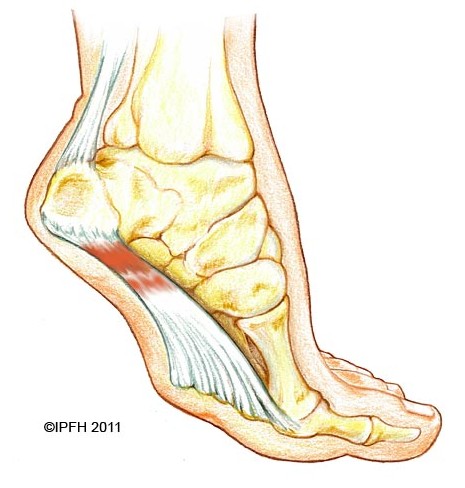
Surgical Treatment
The most dramatic therapy, used only in cases where pain is very severe, is surgery. The plantar fascia can be partially detached from the heel bone, but the arch of the foot is weakened and full function may be lost. Another surgery involves lengthening the calf muscle, a process called gastrocnemius recession. If you ignore the condition, you can develop chronic heel pain. This can change the way you walk and cause injury to your legs, knees, hips and back. Steroid injections and some other treatments can weaken the plantar fascia ligament and cause potential rupture of the ligament. Surgery carries the risks of bleeding, infection, and reactions to anesthesia. Plantar fascia detachment can also cause changes in your foot and nerve damage. Gastrocnemius resection can also cause nerve damage.
Prevention
Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. Losing weight, and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet, can be beneficial for your feet. Wearing appropriate footwear is also important. Ideally, you should wear shoes with a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.
What Can Cause Pain At The Heel

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the structures (of the plantar fascia) on the sole of the foot. The inflammation is caused by excess pressure on the structures on the sole of the foot. The plantar fascia becomes inflamed and tiny rips can occur where it attaches into the inside of the heel bone. It tends to be most painful first thing in the morning, or when standing up after sitting for a while. The area becomes inflamed and swollen, and it is the increase in fluid to the area that accumulates when weight is taken off the area, that then causes the pain on standing. Plantar Fasciitis usually starts gradually with pain on standing after rest. Pain is usually located under the heel or to the inside of the heel. Pain is usually at its worst on standing first thing in the morning. The pain will begin to ease once you get moving. Pain in the early stages tends to occur after activity rather than during activity. As plantar fasciitis continues the pain can become more constant and can then start to affect the way you walk.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder in the lower part of your foot usually around the heel. That pain usually hurts as you get up in the morning when you try to stand on your feet, or after any periods of inactivity. It is a disorder of a tough and strong band that connects the heel bone to the toes. Plantar Fasciitis is caused by injuring that tough band on the bottom of the foot. The following may be the causes of plantar fasciitis. Tight calf muscles or tight Achilles tendon produces repetitive over-stretching of the plantar fascia. Gait and balance Problem may be a dominant cause of this disorder. Many people have a special style of walking, with something unique that causes some kind of imbalance in their body. It might be something like locked knees, feet that turn-out, a weak abdomen etc. This imbalance may place some pressure on the fascia, which eventually causes plantar fasciitis. Weak foot muscles don’t give enough support to the plantar fascia. The small muscles in the foot give the foot its shape by keeping the bones in place and by expanding and contracting to make a movement. Weak foot muscles will allow greater stress on the fascia. Foot anatomical problems such as flat feet or high arches can make the fascia ligament work or stretch abnormally. Flattening of the fat pad at the sole of the feet under the heels is a Degeneration process that is caused by poor footwear or by age. Shoes that have no proper heel cup can flatten that fat pad quite quickly and cause this disorder. Walking in shoes which do not have good arch support is considered to be a cause of plantar fasciitis. Wearing inadequate or worn out shoes may place more stress on the fascia ligament. If you wear shoes that don't fit you by size or width, you may put your feet under excessive stress. Overweight Men and women are more vulnerable to developing the condition because of the excess weight on the foot. Pregnant women are at risk due to gaining weight through pregnancy and due to the pregnancy hormones that make ligaments loosen and relax. Sudden increase of activity like starting to run long distance or complete change of daily activity can cause heel pain and this disorder. Practice of repetitive athletic activities, like long distance running, playing a ball game, dancing or jumping, is a common cause for the disorder. Actually it is considered as one of the most common running injuries. Spending long periods of time on your feet everyday can cause plantar fasciitis. Working on your feet a few hours a day evey day may be the reason for your heel pain.
Symptoms
Patients with plantar fasciitis typically experience pain underneath the heel and along the inner sole of the foot. In less severe cases, patients may only experience an ache or stiffness in the plantar fascia or heel that increases with rest (typically at night or first thing in the morning) following activities which place stress on the plantar fascia. These activities typically include standing, walking or running excessively (especially up hills, on uneven surfaces or in poor footwear such as thongs), jumping, hopping and general weight bearing activity. The pain associated with this condition may also warm up with activity in the initial stages of injury. As the condition progresses, patients may experience symptoms that increase during sport or activity, affecting performance. In severe cases, patients may walk with a limp or be unable to weight bear on the affected leg. Patients with this condition may also experience swelling, tenderness on firmly touching the plantar fascia (often on a specific spot on the inner aspect of the heel) and sometimes pain on performing a plantar fascia stretch.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by a health care provider after consideration of a person’s presenting history, risk factors, and clinical examination. Tenderness to palpation along the inner aspect of the heel bone on the sole of the foot may be elicited during the physical examination. The foot may have limited dorsiflexion due to tightness of the calf muscles or the Achilles tendon. Dorsiflexion of the foot may elicit the pain due to stretching of the plantar fascia with this motion. Diagnostic imaging studies are not usually needed to diagnose plantar fasciitis. However, in certain cases a physician may decide imaging studies (such as X-rays, diagnostic ultrasound or MRI) are warranted to rule out other serious causes of foot pain. Bilateral heel pain or heel pain in the context of a systemic illness may indicate a need for a more in-depth diagnostic investigation. Lateral view x-rays of the ankle are the recommended first-line imaging modality to assess for other causes of heel pain such as stress fractures or bone spur development. Plantar fascia aponeurosis thickening at the heel greater than 5 millimeters as demonstrated by ultrasound is consistent with a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. An incidental finding associated with this condition is a heel spur, a small bony calcification on the calcaneus (heel bone), which can be found in up to 50% of those with plantar fasciitis. In such cases, it is the underlying plantar fasciitis that produces the heel pain, and not the spur itself. The condition is responsible for the creation of the spur though the clinical significance of heel spurs in plantar fasciitis remains unclear.
Non Surgical Treatment
About 90% of plantar fasciitis cases are self-limited and will improve within six months with conservative treatment and within a year regardless of treatment. Many treatments have been proposed for the treatment of plantar fasciitis. First-line conservative approaches include rest, heat, ice, calf-strengthening exercises, techniques to stretch the calf muscles, achilles tendon, and plantar fascia, weight reduction in the overweight or obese, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs are commonly used to treat plantar fasciitis, but fail to resolve the pain in 20% of people. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is an effective treatment modality for plantar fasciitis pain unresponsive to conservative nonsurgical measures for at least three months. Corticosteroid injections are sometimes used for cases of plantar fasciitis refractory to more conservative measures. The injections may be an effective modality for short-term pain relief up to one month, but studies failed to show effective pain relief after three months. Notable risks of corticosteroid injections for plantar fasciitis include plantar fascia rupture, skin infection, nerve or muscle injury, or atrophy of the plantar fat pad. Custom orthotic devices have been demonstrated as an effective method to reduce plantar fasciitis pain for up to 12 weeks. Night splints for 1-3 months are used to relieve plantar fasciitis pain that has persisted for six months. The night splints are designed to position and maintain the ankle in a neutral position thereby passively stretching the calf and plantar fascia overnight during sleep. Other treatment approaches may include supportive footwear, arch taping, and physical therapy.

Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with plantar fasciitis are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don't improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. While the success rate is very high following surgery, one should be aware that there is often a prolonged postoperative period of discomfort similar to the discomfort experienced prior to surgery. This pain usually will abate within 2-3 months. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.
What Leads To Pain Under The Heel

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain. The plantar fascia camera.gif is the flat band of tissue (ligament) that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. If you strain your plantar fascia, it gets weak, swollen, and irritated (inflamed). Then your heel or the bottom of your foot hurts when you stand or walk. Plantar fasciitis is common in middle-aged people. It also occurs in younger people who are on their feet a lot, like athletes or soldiers. It can happen in one foot or both feet.
Causes
Identified risk factors for plantar fasciitis include excessive running, standing on hard surfaces for prolonged periods of time, high arches of the feet, the presence of a leg length inequality, and flat feet. The tendency of flat feet to excessively roll inward during walking or running makes them more susceptible to plantar fasciitis. Obesity is seen in 70% of individuals who present with plantar fasciitis and is an independent risk factor. Studies have suggested a strong association exists between an increased body mass index and the development of plantar fasciitis. Achilles tendon tightness and inappropriate footwear have also been identified as significant risk factors.
Symptoms
People with this condition sometimes describe the feeling as a hot, sharp sensation in the heel. You usually notice the pain first thing in the morning when you stand. After walking for a period of time, the pain usually lessens or even disappears. However, sharp pain in the center of the heel may return after resting for a period of time and then resuming activity.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Heel cups are used to decrease the impact on the calcaneus and to theoretically decrease the tension on the plantar fascia by elevating the heel on a soft cushion. Although heel cups have been found to be useful by some physicians and patients, in our experience they are more useful in treating patients with fat pad syndrome and heel bruises than patients with plantar fasciitis. In a survey of 411 patients with plantar fasciitis, heel cups were ranked as the least effective of 11 different treatments.

Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
What May Cause Painful Heel And How To Remedy It

Overview
Plantar fasciosis is pain at the site of the attachment of the plantar fascia and the calcaneus (calcaneal enthesopathy), with or without accompanying pain along the medial band of the plantar fascia. Diagnosis is mainly clinical. Treatment involves calf muscle and plantar soft-tissue foot-stretching exercises, night splints, orthotics, and shoes with appropriate heel elevation. Syndromes of pain in the plantar fascia have been called plantar fasciitis; however, because there is usually no inflammation, plantar fasciosis is more correct. Other terms used include calcaneal enthesopathy pain or calcaneal spur syndrome; however, there may be no bone spurs on the calcaneus. Plantar fasciosis may involve acute or chronic stretching, tearing, and degeneration of the fascia at its attachment site.
Causes
Repeated small injuries to the fascia (with or without inflammation) are thought to be the cause of plantar fasciitis. The injury is usually near to where the plantar fascia attaches to your heel bone. You are more likely to injure your plantar fascia in certain situations. For example, if you are on your feet for a lot of the time, or if you do lots of walking, running, standing, etc, when you are not used to it. (Plantar fasciitis may be confused with 'Policeman's heel', but they are different. Policeman's heel is plantar calcaneal bursitis - inflammation of the sack of fluid (bursa) under the heel bone. This is not as common as plantar fasciitis.) Also, people with a sedentary lifestyle are more prone to plantar fasciitis. If you have recently started exercising on a different surface, for example, running on the road instead of a track. If you have been wearing shoes with poor cushioning or poor arch support. If you are overweight this will put extra strain on your heel. If there is overuse or sudden stretching of your sole. For example, athletes who increase running intensity or distance; poor technique starting 'off the blocks', etc. If you have a tight Achilles tendon (the big tendon at the bottom of your calf muscles above your heel). This can affect your ability to flex your ankle and make you more likely to damage your plantar fascia. Often there is no apparent cause for plantar fasciitis, particularly in older people. A common wrong belief is that the pain is due to a bony growth or 'spur' coming from the heel bone (calcaneum). Many people have a bony spur of the heel bone but not everyone with this gets plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
The major complaint of those with plantar fasciitis is pain and stiffness in the bottom of the heel. This develops gradually over time. It usually affects just one foot, but can affect both feet. Some people describe the pain as dull, while others experience a sharp pain, and some feel a burning or ache on the bottom of the foot extending outward from the heel. The pain is usually worse in the morning when you take your first steps out of bed, or if you’ve been sitting or lying down for a while. Climbing stairs can be very difficult due to the heel stiffness. After prolonged activity, the pain can flare-up due to increased inflammation. Pain is not usually felt during the activity, but rather just after stopping.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for heel pain usually involves using a combination of techniques, such as stretches and painkillers, to relieve pain and speed up recovery. Most cases of heel pain get better within 12 months. Surgery may be recommended as a last resort if your symptoms don't improve after this time. Only 1 in 20 people with heel pain will need surgery. Whenever possible, rest the affected foot by not walking long distances and standing for long periods. However, you should regularly stretch your feet and calves using exercises such as those described below. Pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can be used to help relieve pain. Some people also find applying an ice pack to the affected heel for 5-10 minutes can help relieve pain and inflammation. However, do not apply an ice pack directly to your skin. Instead, wrap it in a towel. If you do not have an ice pack, you can use a packet of frozen vegetables.

Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.
Stretching Exercises
The following exercises are commonly prescribed to patients with this condition. You should discuss the suitability of these exercises with your physiotherapist prior to beginning them. Generally, they should be performed 2 - 3 times daily and only provided they do not cause or increase symptoms. Your physiotherapist can advise when it is appropriate to begin the initial exercises and eventually progress to the intermediate and advanced exercises. As a general rule, addition of exercises or progression to more advanced exercises should take place provided there is no increase in symptoms. Calf Stretch with Towel. Begin this stretch in long sitting with your leg to be stretched in front of you. Your knee and back should be straight and a towel or rigid band placed around your foot as demonstrated. Using your foot, ankle and the towel, bring your toes towards your head until you feel a stretch in the back of your calf, Achilles tendon, plantar fascia or leg. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times at a mild to moderate stretch provided the exercise is pain free. Resistance Band Calf Strengthening. Begin this exercise with a resistance band around your foot as demonstrated and your foot and ankle held up towards your head. Slowly move your foot and ankle down against the resistance band as far as possible and comfortable without pain, tightening your calf muscle. Very slowly return back to the starting position. Repeat 10 - 20 times provided the exercise is pain free.
Symptoms Of Broken or Fractured Toes
The causes of lip swelling could range from trauma and contact dermatitis to allergic reactions to certain medical conditions. I am a 44 year old Pe teacher who has been experiencing Hallux Valgus since October. Vinegar has been used as a condiment for several centuries.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
Most flat feet usually do not cause pain or other problems. Flat feet may be associated with pronation, a leaning inward of the ankle bones toward the center line. Foot pain, ankle pain or lower leg pain, especially in children, may be a result of flat feet and should be evaluated.
Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa: A condition that causes blistering of the skin because of a mutation of a gene which in normal conditions helps in the formation of thread-like fibers that are anchoring filaments, which fix the epidermis to the basement membrane. Kanner Syndrome: Also referred to as Autism, this is one of the neuropsychiatric conditions typified by deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and abnormally repetitive behavior. Kaposi's Sarcoma: A kind of malignancy of the skin that usually afflicts the elderly, or those who have problems in their immune system, like AIDS. For example, a year of perfect health is regarded as equivalent to 1.0 QALY.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
Most flat feet usually do not cause pain or other problems. Flat feet may be associated with pronation, a leaning inward of the ankle bones toward the center line. Foot pain, ankle pain or lower leg pain, especially in children, may be a result of flat feet and should be evaluated.

Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.

Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa: A condition that causes blistering of the skin because of a mutation of a gene which in normal conditions helps in the formation of thread-like fibers that are anchoring filaments, which fix the epidermis to the basement membrane. Kanner Syndrome: Also referred to as Autism, this is one of the neuropsychiatric conditions typified by deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and abnormally repetitive behavior. Kaposi's Sarcoma: A kind of malignancy of the skin that usually afflicts the elderly, or those who have problems in their immune system, like AIDS. For example, a year of perfect health is regarded as equivalent to 1.0 QALY.