What Is Plantar Fasciitis

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is sometimes mixed up with a heel spur although they are not the same. A heel spur is a calcium deposit that occurs where the plantar fascia is attached to the heel bone (calcaneus). In many cases a heel spur is found on a foot with no pain or other symptoms at all. And in many painful heels there is no sign for a heel spur. Heel spur and painful heal does not necessarily go together. For many years plantar fasciitis was believed to be an inflammatory condition. It is thought now to be inaccurate because there were many cases of the disorder with no inflammatory signs observed within the fascia. The heel pain cause is now believed to be damage to the collagen fibers of the fascia. This damage, caused by stress injury, sometimes may include inflammatory cells.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the thick band of tissue on the bottom of the foot is overstretched or overused. This can be painful and make walking more difficult. You are more likely to get plantar fasciitis if you Have foot arch problems (both flat feet and high arches), run long distances, downhill or on uneven surfaces, are obese or gain weight suddenly, have a tight Achilles tendon (the tendon connecting the calf muscles to the heel), wear shoes with poor arch support or soft soles. Plantar fasciitis is seen in both men and women. However, it most often affects active men ages 40 - 70. It is one of the most common orthopedic foot complaints. Plantar fasciitis was commonly thought to be caused by a heel spur. However, research has found that this is not the case. On x-ray, heel spurs are seen in people with and without plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis is usually found in one foot. While bilateral plantar fasciitis is not unheard of, this condition is more the result of a systemic arthritic condition that is extremely rare in an athletic population. There is a greater incidence of plantar fasciitis in males than females (Ambrosius 1992). While no direct cause could be found it could be argued that males are generally heavier which, when combined with the greater speeds, increased ground contact forces, and less flexibility, may explain the greater injury predisposition. The most notable characteristic of plantar fasciitis is pain upon rising, particularly the first step out of bed. This morning pain can be located with pinpoint accuracy at the bony landmark on the anterior medial tubercle of the calcaneus. The pain may be severe enough to prevent the athlete from walking barefooted in a normal heel-toe gait. Other less common presentations include referred pain to the subtalar joint, the forefoot, the arch of the foot or the achilles tendon (Brantingham 1992). After several minutes of walking the pain usually subsides only to re turn with the vigorous activity of the day's training session. The problem should be obvious to the coach as the athlete will exhibit altered gait and/ or an abnormal stride pattern, and may complain of foot pain during running/jumping activities. Consistent with plantar fascia problems the athlete will have a shortened gastroc complex. This can be evidenced by poor dorsiflexion (lifting the forefoot off the ground) or inability to perform the "flying frog" position. In the flying frog the athlete goes into a full squat position and maintains balance and full ground contact with the sole of the foot. Elevation of the heel signifies a tight gastroc complex. This test can be done with the training shoes on.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will check your feet and watch you stand and walk. He or she will also ask questions about your past health, including what illnesses or injuries you have had. Your symptoms, such as where the pain is and what time of day your foot hurts most. How active you are and what types of physical activity you do. Your doctor may take an X-ray of your foot if he or she suspects a problem with the bones of your foot, such as a stress fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment initially involves offloading the plantar fascia by aoiding aggravating factors, such as running. Taping, this can work very well to alleviate pain, and can be almost immediate. It isn't a long-term solution, but can relieve symptoms in the beginning. Using a night splint to stretch the calf, so that less load is placed on the plantar fascia (if tightness in the calf is a factor). Using a gel heel cup, this can act to increase shock absorption, and by raising the heel there is also less stretch on the calf. So, temporarily, this may relieve pain in someone who has a tight calf. Massage, but this depends if the plantarfascia is actually tight or just painful. If it is tight, then massage can temporarily relieve the pain, but if it is irritated then taping and corrective footwear is preferable.
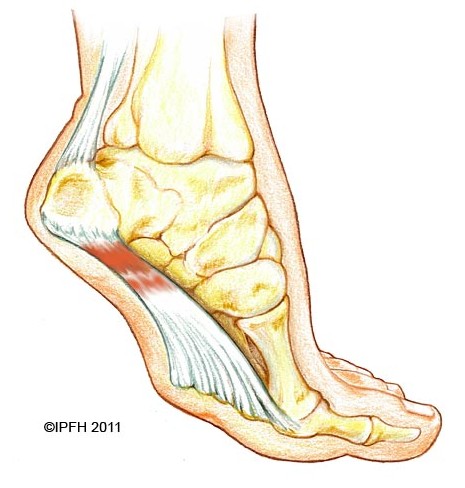
Surgical Treatment
The most dramatic therapy, used only in cases where pain is very severe, is surgery. The plantar fascia can be partially detached from the heel bone, but the arch of the foot is weakened and full function may be lost. Another surgery involves lengthening the calf muscle, a process called gastrocnemius recession. If you ignore the condition, you can develop chronic heel pain. This can change the way you walk and cause injury to your legs, knees, hips and back. Steroid injections and some other treatments can weaken the plantar fascia ligament and cause potential rupture of the ligament. Surgery carries the risks of bleeding, infection, and reactions to anesthesia. Plantar fascia detachment can also cause changes in your foot and nerve damage. Gastrocnemius resection can also cause nerve damage.
Prevention
Being overweight can place excess pressure and strain on your feet, particularly on your heels. Losing weight, and maintaining a healthy weight by combining regular exercise with a healthy, balanced diet, can be beneficial for your feet. Wearing appropriate footwear is also important. Ideally, you should wear shoes with a low to moderate heel that supports and cushions your arches and heels. Avoid wearing shoes with no heels.